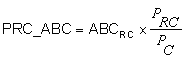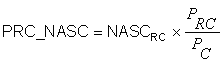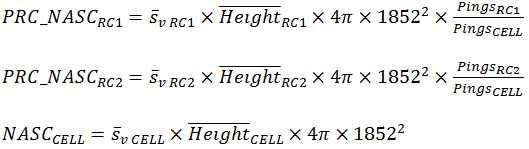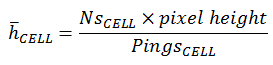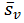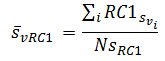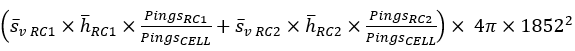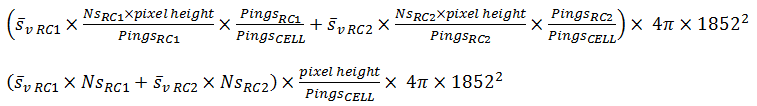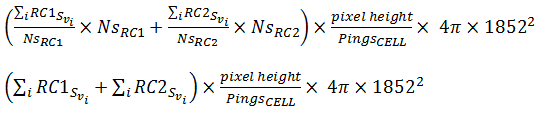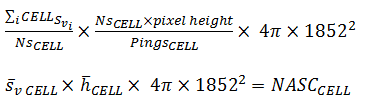PRC_ABC and PRC_NASC
PRC_ABC and PRC_NASC enable you to use region-based classification on your data, integrate the regions in the cells and then estimate biomass with respect to your region classifications. All without requiring the use of virtual variables.
PRC_ABC and PRC_NASC represent the contribution of the region-cell intersection (RC) to the ABC or NASC respectively of the cell (C) that contains the region cell intersection (RC). They are only meaningful and are only output when integrating by regions by cells, i.e. when the analysis domain is a region-cell intersection.
Hint: "PRC" is a mnemonic for "Proportion that the Region contributes to Cell".
|
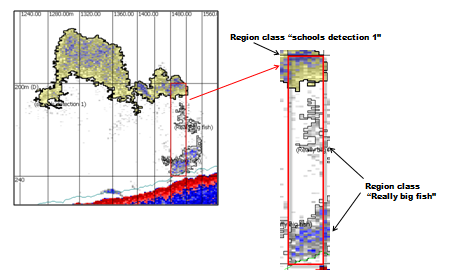
Screen shot of part of the AutoOpen.EV Sv pings echogram with regions achieved by using a 2D school detection and then applying a region classification rule. Three regions are shown:
A cell is marked in red with an inset that displays greater detail of the regions that contribute to the cell. The grid units are 40m distance by 40m depth. |
 |
- PRC_ABC
- PRC_NASC
- Additivity (includes a worked example for two regions that fill a cell)
PRC_ABC (PRC Area Backscattering Coefficient - m2m-2)
Let ABCC be the ABC of a domain C defined by a cell.
Let ABCRC be the ABC of a domain RC defined by a region-cell intersection.
Then PRC_ABC is defined as:
|
|
Where:
PRC = Number of pings in the domain RC
PC = Number of pings in the domain C
PRC_NASC (PRC Nautical Area Scattering Coefficient - m2nmi-2)
PRC_NASC is defined in the same way as PRC_ABC above and accordingly:
|
|
|
Notes:
- ABCRC and NASCRC are not output by Echoview.
- Changes to the Exclusions and Analysis settings on the Analysis page of the Variable Properties dialog box can reduce the Thickness_mean and hence the volume that NASC is valid over. Changes to the Threshold settings of the Data page of the Variable Properties dialog box may change data values in the analysis domain. Such changes can affect the Echoview values for Sv_mean and/or Thickness_mean and the final NASC value. For more information refer to About samples and echo integration.
- Care is required when using Exclusions settings, stray bottom signal (associated with an Exclude below line) can introduce large errors to the calculated NASC.
Additivity
The powerful feature of PRC_ABC and PRC_NASC, is that it is possible to meaningfully add all PRC_ABC values in one interval or cell. The same holds true for PRC_NASC. If a cell is completely divided into i regions, such that none of the regions overlap and all of the samples in that cell fall within one of the regions, then the sum of all the PRC_ABCi is equal to the ABC of the cell. Similarly, the sum of all the PRC_NASCi is equal to the NASC of the cell.
Note: The Regions page of the Cell integration dialog box displays PRC_NASC for the cell.
Worked example
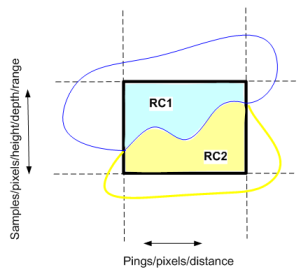
Diagram of a cell (heavy outline) on an echogram with region-cell intersections RC1 and RC2.
For case where the region cell intersections completely fill the cell, the additivity assertion can be expressed as:
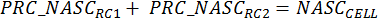 |
(1) |
||||||||||||
|
|
(2) |
||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
Add the PRC_NASC in the CELL
|
(3) |
||||||||||||
|
Re-express
|
(4) |
||||||||||||
|
|
(5) |
||||||||||||
|
This becomes
This result accounts for height, samples and pixels in the cell and region-cell intersections. |
(6) |